Multirotor vs Fixed Wing vs VTOL UAV: What’s the Difference?
In the rapidly evolving world of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), three main types dominate the skies: multirotor, fixed-wing, and VTOL (Vertical Take-Off and Landing) drones. Each type of UAV offers distinct advantages and serves specific applications, making them invaluable tools across various industries. Understanding the differences between these UAVs is essential for selecting the right drone for your needs, whether it's for aerial photography, surveying, or cargo delivery. This article delves into the unique characteristics, advantages, and applications of multirotor, fixed-wing, and VTOL drones, providing a comprehensive comparison to help you make an informed decision.
What is a multirotor drone?
A multirotor drone, commonly referred to as multicopter or a multirotor UAV, is an aircraft that is lifted and propelled by multiple rotors. These drones come in various configurations, typically featuring three (tricopter), four (quadcopter), six (hexacopter), or eight (octocopter) rotors. These rotors are fixed-wing and spin continuously to generate lift. Unlike traditional helicopters that use complex variable-pitch rotors, multirotors can change the speed of each rotor to control flight direction. Their ability to provide stable flight, hover precisely, and operate in diverse environments makes multirotor drones a popular choice for both commercial and recreational purposes.
What are the main components of a multirotor drone?
●Frame: The structural body of the drone, which holds all the components together. It is typically made from lightweight materials like carbon fiber or aluminum.
Motors: The propulsion system of the drone, responsible for generating lift and enabling flight. Multirotors have multiple motors, typically arranged in pairs (quadcopters have 4, hexacopters have 6, etc.).
●Propellers: Attached to the motors, propellers create thrust to lift and maneuver the drone. They come in pairs of clockwise (CW) and counter-clockwise (CCW) rotating types to balance the drone.
●Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs): Devices that control the speed of the motors based on signals from the flight controller. They regulate the power supplied to the motors.
●Flight Controller: The central brain of the drone, processing input from sensors and the remote control to stabilize and navigate the drone. It manages motor speed and adjusts for stable flight.
●Battery: The power source for the drone, usually a lithium-polymer (LiPo) battery, providing the necessary energy for the motors and electronics.
●Radio Receiver: Receives control signals from the pilot’s remote control (transmitter) and sends them to the flight controller.
●Transmitter: The transmitter is a handheld device that the pilot uses to control the drone. It sends signals to the receiver, which tells the flight controller how to move the drone.
In addition to these main components, some multirotor drones may also include additional components such as camera, gimbal and GPS module.
How does a multirotor drone work?
Multirotor drones work by varying the speed of their rotors to control lift and movement. The flight controller processes input from the pilot and sensors to adjust motor speeds, ensuring stable flight.
●Rotors for lift: Each rotor is connected to a motor that spins it rapidly. As the rotors spin, they create lift, much like how a helicopter's rotor blades lift it off the ground.
●Flight control: The brain of the drone is the flight controller, which is a circuit board with sensors and processors. It receives input from gyroscopes and accelerometers that detect the drone's orientation and movement. Based on this information, the flight controller sends signals to the Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs) to adjust the speed of each motor accordingly. The pilot's control inputs from the transmitter are also factored in to achieve the desired flight path.
●Stability and control: By varying the speed of each motor, the drone can control its altitude, direction, and movement. The rotors on one side of the drone can be sped up to generate more lift on that side. This tilts the drone in that direction. Conversely, slowing down rotors on one side tilts the drone in the opposite direction. By speeding up opposing motors diagonally, the drone can rotate on its axis (yaw). Adjusting the speed of all motors simultaneously will cause the entire drone to rise or descend.
●Battery power: Multirotor drones are powered by batteries, which provide electricity to the motors. The flight time of a drone is limited by the capacity of its battery and the efficiency of its motors.
What are the types of multirotor drones?
Multirotor drones come in various configurations, primarily distinguished by the number of rotors they have. Here are the main types:
Tricopters
A tricopter is a type of multirotor drone that has three rotors arranged in a triangular shape.They are known for their simple design, lightweight build, and maneuverability.Tricopters are an interesting choice for enthusiasts looking for a balance between simplicity and performance, particularly in DIY drone projects.

Quadcopters
A quadcopter is a type of multirotor drone that is powered by four rotors, arranged in an "X" or "+" configuration. Each rotor consists of a motor and a propeller, and the quadcopter's movement is controlled by varying the speed of these rotors. This is the most popular type of multirotor drone due to its simple design, stability, and ease of control.
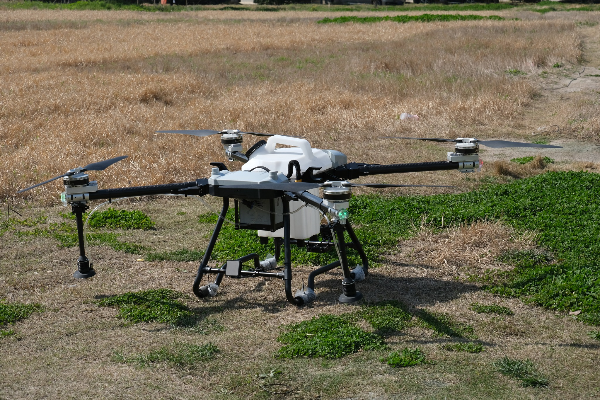

Hexacopters
A hexacopter is a type of multirotor drone that has six rotors, arranged in a hexagonal shape. The term "hexacopter" combines "hexa," meaning six, and "copter," derived from helicopter. These drones can carry heavier payloads than quadcopters due to the additional lift generated by the extra rotors.

Octocopters
An octocopter is a type of multirotor drone that has eight rotors. These rotors are typically arranged in a symmetrical pattern, which can be in various configurations such as a plus (+) or an X shape. These drones are very stable and can carry even heavier payloads than hexacopters, which makes them suitable for professional and industrial uses where carrying heavier payloads and ensuring flight reliability are critical.

What are the advantages and disadvantages of multirotor drones?
Multirotor drones offer a unique set of advantages and disadvantages compared to other drone designs. Here's a breakdown of the key points:
Advantages of Multirotor Drones
●Maneuverability: Multirotors can hover in place, fly in any direction, and perform complex aerial maneuvers. This makes them ideal for tasks that require precise positioning and movement, such as aerial photography, inspection, and surveillance.
●Vertical Takeoff and Landing (VTOL): They can take off and land vertically, which means they don’t require a runway. This is advantageous in urban environments or confined spaces.
●Ease of Control: Their design allows for stable flight and easy control, even for beginners. Many come with advanced flight control systems and GPS stabilization.
●Compact Size: Many multirotors are compact and portable, making them easy to transport and deploy in various locations. This is a major advantage for applications where portability is important, such as search and rescue or aerial photography.
Disadvantages of Multirotor Drones
●Limited Flight Time: Multirotors generally have shorter flight times compared to fixed-wing drones due to higher power consumption needed to maintain lift. Most consumer models have flight times ranging from 20 to 30 minutes.
●Lower Speed and Range: They are typically slower and have a shorter range than fixed-wing drones, which limits their effectiveness for long-distance missions.
●Payload Limitations: While they can carry various payloads, their payload capacity is often lower than that of fixed-wing or larger VTOL drones, limiting the weight and size of equipment they can transport.
●Sensitivity to Wind: Multirotors are more affected by wind and weather conditions compared to fixed-wing drones, which can impact stability and flight performance.
How can you extend the flight time of a multirotor drone?
Extending the flight time of a multirotor drone can be achieved through several methods:
●Optimize the Weight: Reduce the overall weight of the drone by using lightweight materials for the frame and components. This reduces the power needed to lift the drone, thus increasing flight time.
●Battery Capacity: Use high-capacity lipo batteries with a higher energy density. Look for batteries with a high mAh rating, but choose one that offers the best balance of capacity and weight for your drone. Grepow's UAV batteries, for example, offer higher capacities that can extend flight times.
●Efficient Propellers: Choose propellers that are designed for efficiency rather than speed. Larger propellers with a lower pitch can increase efficiency and lift, extending flight time.
●Aerodynamics: Improve the drone's aerodynamics by using streamlined designs and reducing drag. This can improve efficiency and extend flight time.
What is a multirotor used for?
Multirotors, like quadcopters, hexacopters, and octocopters, are used for a variety of purposes due to their versatility, stability, and ease of control. Some common uses include:
●Aerial Photography and Videography: Multirotors are widely used for capturing photos and videos from the air, providing stunning aerial views for filmmaking, real estate, construction, and tourism industries.
●Surveillance and Security: Multirotors equipped with cameras and other sensors are used for monitoring and surveillance purposes. They can identify potential problems with roofs, chimneys, or power lines, reducing the risks involved in sending inspectors up high.
●Search and Rescue: Due to their ability to access hard-to-reach areas, multirotors are used in search and rescue operations to locate missing persons or assess the extent of a disaster.
●Mapping and Surveying: Multirotors are used for mapping terrain, surveying land, and creating 3D models of landscapes, which is valuable for urban planning, agriculture, and environmental monitoring.
●Agriculture: Multirotors equipped with specialized cameras and sensors are used in precision agriculture for tasks like crop monitoring, spraying pesticides, and assessing plant health. Delivery and Logistics: With advancements in drone technology, multirotors are being explored for delivering small packages and goods in urban and remote areas, offering faster and more efficient delivery options.
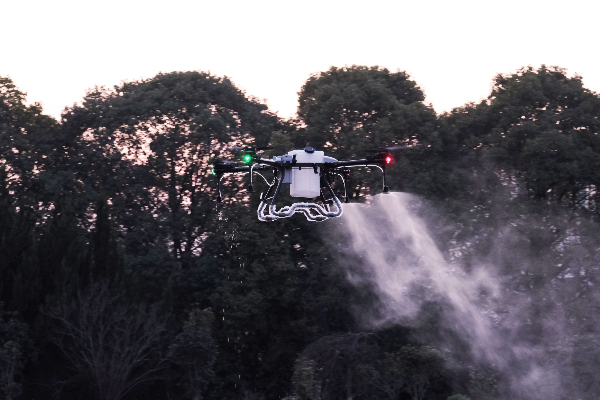

●Recreation and Racing: Many hobbyists enjoy flying multirotors for fun, while others participate in drone racing events, where speed and agility are key.
What safety precautions should be taken when flying a multirotor drone?
Flying a multirotor drone safely involves several precautions to protect yourself, others, and the drone itself:
●Check Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with the drone laws and regulations in your area, including where you are allowed to fly and any restrictions that apply.
●Pre-Flight Checklist: Always perform a pre-flight check of your drone, including checking the battery, propellers, and other components for any damage or loose connections.
●Safe Flying Area: Fly in an open area away from people, buildings, and other obstacles. Avoid flying over crowds or near airports.
●Maintain Line of Sight: Keep your drone within your line of sight at all times to avoid collisions with other objects or aircraft.
●Respect Privacy: Avoid flying over private property without permission and respect people's privacy.
●Weather Conditions: Avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or other adverse weather conditions that could affect the drone's stability.
What is a Fixed-Wing drone?
A fixed-wing drone, also known as fixed-wing UAVs, is an aircraft with a rigid wing that generates lift through forward motion. Unlike multirotor drones, which achieve lift and propulsion through rotating propellers, fixed-wing drones generate lift through their aerodynamic design, enabling them to fly more efficiently and cover longer distances.
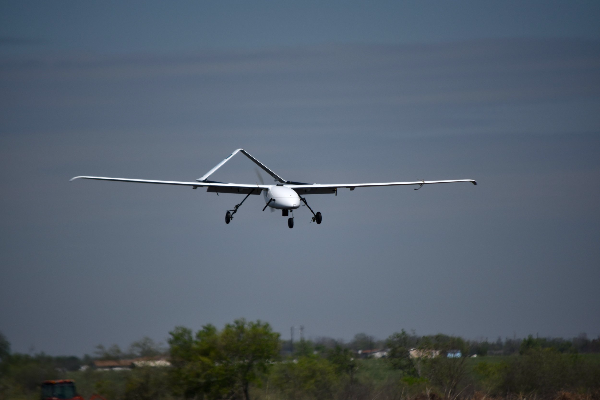

What is the difference between fixed-wing and rotary-wing?
Fixed-wing and rotary-wing refer to different types of aircraft based on their wing configuration and method of lift. The main difference between fixed-wing and rotary-wing aircraft lies in how they generate lift to fly. Fixed-wing aircraft require forward motion to generate lift and primarily use control surfaces for maneuverability, while rotary-wing aircraft can hover and lift vertically, with control achieved by varying the pitch of rotor blades.
Fixed-Wing Aircraft
●These aircraft have wings that generate lift as they move through the air.
●They require forward motion (speed) to generate lift.
●Control is primarily achieved through the use of control surfaces such as ailerons, elevators, and rudders.
●Examples include airplanes, gliders, and some drones.
Rotary-Wing Aircraft
●These aircraft have wings that rotate to generate lift, commonly known as rotor blades.
●They can achieve lift and hover without the need for forward motion.
●Control is achieved by varying the pitch of the rotor blades.
●Examples include helicopters and some types of drones, like quadcopters.
Is a helicopter a fixed-wing aircraft?
A helicopter is not a fixed-wing aircraft. Helicopters are categorized as rotary-wing aircraft because they achieve lift and thrust through one or more horizontally-spinning rotors. Helicopters are well-suited for missions requiring vertical lift and precision, such as search and rescue, medical evacuation, and urban air mobility. Fixed-wing aircraft excel in long-distance travel, endurance missions, and high-speed operations. Here are the key differences between helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft:
Lift and Thrust Mechanism
●Helicopters: Use spinning rotors to generate lift and thrust, allowing for vertical takeoff and landing, hovering, and agile maneuvers.
●Fixed-Wing Aircraft: Use fixed wings to generate lift through forward motion, typically powered by propellers or jet engines. They require a runway for takeoff and landing.
Structure
●Helicopters: Have a main rotor and usually a tail rotor (or other mechanisms) to counteract torque.
●Fixed-Wing Aircraft: Have stationary wings and control surfaces (e.g., ailerons, elevators, rudders) for stability and control.
Operational Capabilities
●Helicopters: Capable of vertical takeoff and landing, hovering in place, and flying in any direction (forward, backward, sideways).
●Fixed-Wing Aircraft: Require runways or catapult systems for takeoff and landing, generally fly forward, and cannot hover.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Fixed-Wing drones?
Fixed-wing drones offer several advantages over other drone types, but also come with some drawbacks. Here's a breakdown of the key pros and cons:
Advantages of Fixed-Wing Drones
●Longer Flight Times: Fixed-wing drones can glide and use less energy to stay aloft, resulting in longer flight durations compared to multirotor drones.
●Greater Range: They can cover larger areas in a single flight, making them ideal for applications like surveying, mapping, and agricultural monitoring.
●Higher Speeds: Fixed-wing drones can achieve higher speeds, which is beneficial for tasks requiring quick coverage of vast areas.
●Payload Capacity: Many fixed-wing drones are designed to carry larger payloads, making them suitable for professional-grade cameras and sensors.
Disadvantages of Fixed-Wing Drones
●Takeoff and Landing Requirements: They typically require a runway or a catapult for takeoff and landing, which limits their use in confined spaces.
●Maneuverability: Fixed-wing drones are less maneuverable than multirotor drones, making them less suitable for tasks that require hovering or intricate movement.
●Limited VTOL Capability: Without additional mechanisms, fixed-wing drones cannot take off and land vertically, limiting their versatility in some applications.
What is the average flight time and range of fixed-wing drones?
The average flight time and range of fixed-wing drones can vary widely depending on their design, purpose, and payload. These figures can be influenced by factors such as battery capacity, weight, aerodynamic efficiency, and environmental conditions.
Average Flight Time
●Consumer and Prosumer Fixed-Wing Drones: Typically have flight times ranging from 1 to 2 hours.
●Commercial and Industrial Fixed-Wing Drones: Often achieve flight times of 2 to 6 hours, with some high-end models capable of flying for 12 hours or more.
Average Range
●Consumer and Prosumer Fixed-Wing Drones: Usually have a range of 50 to 100 kilometers (31 to 62 miles).
●Commercial and Industrial Fixed-Wing Drones: Can cover distances of 100 to 200 kilometers (62 to 124 miles), with some capable of exceeding 500 kilometers (310 miles) under optimal conditions.
Fixed Wing UAV Applications
Fixed-wing UAVs are highly versatile and are used in a wide range of applications due to their efficiency and long endurance. Here are some common applications:
●Aerial Mapping and Surveying: Fixed-wing UAVs can cover large areas quickly and efficiently, making them ideal for creating detailed maps and conducting surveys in agriculture, forestry, and urban planning.
●Agriculture: Used for crop monitoring, precision agriculture, and spraying. They help in assessing crop health, monitoring irrigation systems, and applying fertilizers or pesticides.
●Environmental Monitoring: Deployed for monitoring wildlife, tracking environmental changes, and assessing the health of ecosystems. They are also used for disaster response, such as assessing damage after natural disasters.
●Surveillance and Security: Utilized by law enforcement for border patrol, surveillance missions, and monitoring large events. They provide real-time intelligence and situational awareness.
●Delivery Services: Employed in logistics for delivering goods, especially in remote or difficult-to-reach areas. Fixed-wing UAVs offer longer range and higher payload capacities compared to multirotor drones.
How Does a Fixed-Wing UAV Fly?
Fixed-wing UAVs fly using principles similar to those of manned fixed-wing aircraft. Here's a step-by-step overview of how they achieve and sustain flight:
1. Lift Generation
●Wings: Fixed-wing UAVs have wings that generate lift. As the UAV moves forward, air flows over and under the wings. The shape of the wings (airfoil design) creates a pressure difference, with lower pressure on top and higher pressure on the bottom, generating lift.
2. Thrust Production
●Propulsion System: Fixed-wing UAVs use a propulsion system, typically a propeller driven by an electric motor or an internal combustion engine. The propulsion system generates thrust, propelling the UAV forward and enabling airflow over the wings.
3. Control Surfaces
●Ailerons: Located on the wings, ailerons control roll, allowing the UAV to tilt and turn left or right.
●Elevators: Found on the tail, elevators control pitch, allowing the UAV to climb or descend.
●Rudder: Also on the tail, the rudder controls yaw, enabling the UAV to steer left or right.
4. Flight Dynamics
●Takeoff: The UAV gains speed on the ground or from a hand launch. Once it reaches a sufficient speed, the lift generated by the wings exceeds the weight of the UAV, allowing it to take off.
●Climb: To climb, the UAV increases its thrust and adjusts the elevators to raise the nose, increasing the angle of attack and generating more lift.
●Cruise: During cruising flight, the UAV maintains a steady altitude and speed. The lift balances the weight, and the thrust balances the drag (air resistance).
● Maneuvering: By adjusting the control surfaces (ailerons, elevators, rudder), the UAV can turn, climb, descend, and perform other maneuvers.
●Descent and Landing: To land, the UAV reduces thrust and adjusts the elevators to lower the nose. It descends gradually and touches down, reducing speed until it comes to a stop.
5. Autopilot and Navigation Systems
●Autopilot: Many fixed-wing UAVs are equipped with autopilot systems that control the flight path, altitude, and speed based on pre-programmed flight plans or real-time commands from a ground control station.
●Navigation: GPS and other navigation systems help the UAV maintain its course and reach its destination accurately.
6. Stability and Control
●Gyroscopes and Accelerometers: These sensors provide data to the flight control system to maintain stability and control during flight.
●Flight Control Software: Algorithms process sensor data and control surface adjustments to ensure smooth and stable flight, compensating for wind and other environmental factors.
What Is a VTOL UAV?
VTOL stands for Vertical Take-Off and Landing. This term is used to describe aircraft that have the capability to take off, hover, and land vertically, without the need for a conventional runway. VTOL aircraft combine the advantages of fixed-wing airplanes (speed, range, efficiency) with the vertical lift and landing capabilities of helicopters. This makes them highly versatile for various applications, especially in environments where traditional runways are unavailable or impractical. Examples of VTOL aircraft include helicopters, tiltrotor aircraft, and some fixed-wing drones with VTOL capabilities.
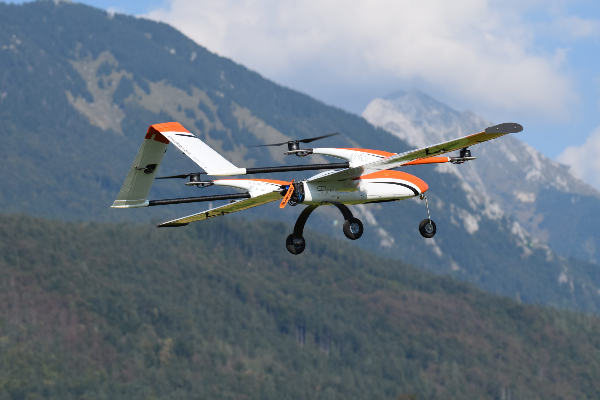

What is the difference between VTOL and eVTOL?
The primary difference between VTOL and eVTOL lies in their propulsion systems:
VTOL:
●Definition: VTOL refers to any aircraft that can take off, hover, and land vertically.
●Propulsion: VTOL aircraft can use various types of propulsion systems, including traditional combustion engines, jet engines, or hybrid systems.
●Examples: Helicopters, tiltrotor aircraft like the V-22 Osprey, and some drones.
eVTOL:
●Definition: eVTOL specifically refers to VTOL aircraft that are powered by electric propulsion systems.
●Propulsion: eVTOL aircraft use electric motors powered by batteries, fuel cells, or hybrid electric systems.
●Examples: Emerging urban air mobility vehicles such as those being developed by companies like Joby Aviation, Archer Aviation, and Lilium.

In summary, while VTOL is a broad category that includes any vertical takeoff and landing aircraft, eVTOL is a subset that exclusively includes those powered by electric propulsion.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of VTOL UAV?
VTOL UAVs offer a unique blend of capabilities, but also come with some drawbacks. Here's a breakdown of the key advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages of VTOL UAVs
●Vertical Takeoff and Landing: VTOL UAVs can take off and land vertically, eliminating the need for runways or launch/landing pads. This allows them to operate in confined spaces or rugged terrain, increasing their flexibility and usability.
●Hover Capability: VTOL UAVs can hover in place, which is useful for tasks that require stationary observation or precise positioning, such as surveillance, mapping, or inspection.
Disadvantages of VTOL UAVs
●Complexity: VTOL UAVs are generally more complex than fixed-wing or multirotor drones, requiring sophisticated control systems for vertical and horizontal flight modes. This complexity can lead to higher costs, maintenance requirements, and potential points of failure.
●Cost: Due to the more intricate mechanisms, VTOL UAVs tend to be more expensive than simpler multi-rotor drones.
How do VTOL UAVdiffer from traditional fixed-wing UAV?
VTOL UAVs differ from traditional fixed-wing UAVs primarily in their takeoff and landing capabilities. Here are the key differences:
●Takeoff and Landing: VTOL UAVs can take off vertically like a helicopter, without needing a runway. They can also land vertically, which can be useful in confined or unprepared spaces. Fixed-wing UAVs, on the other hand, require a runway for takeoff and landing.
●Flight Transition: VTOL UAVs can transition from vertical takeoff to horizontal flight, and vice versa, during the flight. This allows them to combine the benefits of vertical takeoff and landing with the efficiency of fixed-wing flight. Fixed-wing UAVs are optimized for forward flight and do not have vertical takeoff or landing capabilities.
●Flight Efficiency: Fixed-wing UAVs are generally more efficient in forward flight compared to VTOL UAVs. Once in the air, fixed-wing UAVs require less power to maintain flight, allowing them to cover longer distances and stay in the air for extended periods. VTOL UAVs often have shorter flight times and are less efficient for long-range missions.
●Payload Capacity: VTOL UAVs often have a lower payload capacity compared to fixed-wing UAVs of similar size. This is due to the additional weight and complexity of the VTOL mechanism.
Flight Stability: Fixed-wing UAVs tend to be more stable in flight, especially in windy conditions, compared to VTOL UAVs. VTOL UAVs can be more susceptible to gusts of wind during takeoff and landing.
●Mission Flexibility: VTOL UAVs offer greater mission flexibility, as they can operate in a wider range of environments and terrain types. They can take off and land in confined spaces, making them suitable for urban or rugged terrain where a runway is not available.
Is a helicopter a VTOL?
A helicopter is a type of VTOL aircraft. VTOL aircraft can take off, land, and hover vertically, as opposed to traditional airplanes that require a runway for takeoff and landing. Helicopters achieve vertical flight through the use of rotor blades that generate lift.
How does aVTOL drone work?
An electric Vertical Takeoff and Landing drone typically works using a combination of vertical lift and horizontal thrust mechanisms, enabling it to take off, hover, and land vertically like a helicopter, while also having the ability to transition to a more efficient fixed-wing flight for longer-range and higher-speed operations.
●Multi-rotor drones: These are the most common type of VTOL drone. They use multiple rotors, typically four, six, or eight, to generate lift and control their flight. Each rotor spins to push air down, and the reaction force from the air pushes the drone up. By tilting the rotors slightly, the drone can move forward, backward, left, or right. This is similar to how a helicopter works, but with multiple smaller rotors instead of one large one.
●Fixed-wing VTOL drones: These are a newer type of drone that combines features of both helicopters and airplanes. They have fixed wings for aerodynamic lift during horizontal flight, but also have rotors or tilting engines that allow them to take off and land vertically. During takeoff, the rotors or engines provide vertical lift, and then they tilt forward to provide thrust for horizontal flight like a normal airplane. This design allows for longer range and faster flight compared to multi-rotor drones, but can be more complex and expensive.
What are the current applications of VTOL UAV?
●Urban air mobility (passenger transport)
Urban air mobility (UAM) is indeed one of the most prominent and exciting applications of VTOL aircraft. VTOLs in this context are being developed to provide on-demand air transportation services within urban and suburban areas, aiming to alleviate ground transportation congestion and offer faster, more efficient travel options. Several companies are actively working on developing VTOLs for this purpose, with plans to revolutionize the way people commute in densely populated areas.
●Search and rescue
VTOL UAVs can quickly navigate to hard-to-reach or dangerous areas to search for missing persons or survivors in disasters such as earthquakes, floods, or avalanches. Equipped with cameras, thermal imaging, and other sensors, they can provide real-time data to rescuers, helping them locate and assist people in distress.
●Cargo delivery
Cargo delivery is indeed a significant application of VTOL UAVs. These drones can access remote or difficult-to-reach areas, making them ideal for delivering cargo to locations where traditional transportation methods are impractical or unavailable. VTOL UAVs can be used for various types of cargo delivery, including medical supplies, food, and other essential goods, especially in emergency situations or areas with inadequate infrastructure. They can also be used for delivering packages in urban areas, providing a faster and more flexible alternative to traditional delivery services.
●Surveillance and reconnaissance
VTOL UAVs are used for monitoring and reconnaissance in law enforcement and security operations. They can provide real-time video and data from vantage points that are otherwise difficult to access.
Conclusion
As technology continues to advance, the capabilities and applications of UAVs expand, offering new possibilities for innovation and efficiency. Multirotor drones, with their exceptional maneuverability and ease of use, are ideal for tasks requiring precision and agility. Fixed-wing drones excel in long-range and endurance missions, providing unmatched efficiency for large-scale surveys and monitoring. VTOL drones combine the best of both worlds, offering versatility and the ability to operate in diverse environments. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each type, users can choose the most suitable UAV for their specific requirements, harnessing the power of these remarkable technologies to achieve their goals. Whether for commercial, industrial, or personal use, the right drone can transform how we see and interact with the world around us. As a global leading lipo battery manufacturer, Grepow offers professional customizable UAV battery solutions to meet the needs of all knids of multirotor, fixed-wing and VTOL drone applications. If you have any questions or needs, please feel free to contact us at info@grepow.com.
Related Articles:
How to Choose an Aerial Photography Drone?
Some Common Sense about Delivery Drones
Agricultural Drone Common Sense
What is a drone light show and how much does it cost?
How to Choose LiPo Battery for Drone?
Related Articles
-

Powering Aerial Artistry: Grepow Battery Solutions Behind Drone Light Shows
2025-10-27 -

Vatican Drone Show: Where Technology Meets Faith
2025-09-15 -

Why Do We Need Silent Drones?
2025-09-02
Related products
-

Tattu 6S 28000mAh 22.2V 25C Lipo Drone Battery
-

Tattu G-Tech 25C 6S 30Ah 22.2V Lipo Drone Battery
-

Tattu 6S 32Ah 22.8V 10C HV Lipo Drone Battery
-

Tattu 6S 40Ah 22.8V 10C HV Lipo Drone Battery
-

Tattu 3.0 14S 28000mAh 53.2V 25C HV Lipo Smart Drone Battery
-

Tattu 3.0 14S 25000mAh 51.8V 25C Lipo Smart Drone Battery
-

Tattu 4.0 14S 30Ah HV 35C 53.2V Lipo Smart Drone Battery
-

Tattu 4.0 18S Lipo 30Ah 68.4V Smart UAV Drone Battery