RFID Tags Battery Guide
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected through the Internet of Things (IoT), the demand for efficient and reliable tracking systems has never been higher. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags, particularly those powered by batteries, play a crucial role in this landscape. From tracking merchandise to monitoring livestock and even safeguarding patients, RFID technology offers unparalleled advantages in various applications. This guide explores the fundamentals of RFID tags, with a focus on battery-powered, or Active RFID tags, and delves into the RFID tag batteries that are driving the future of these devices.
What is a RFID Tag?
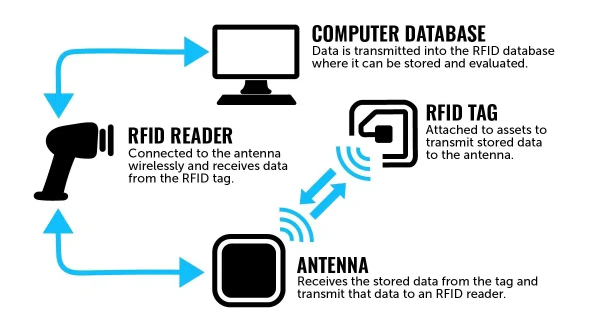
Radio Frequency Identification or RFID is a specific type of radio technology that uses radio waves to identify tags attached to an object and thus identify the object. An RFID system consists of a RFID tag, a RFID reader and an Antenna. These radio waves transmit data from the tag to a reader, which then transmits the information to an RFID computer program. RFID tags are frequently used for merchandise, but they can also be used to track vehicles, livestocks, pets, and even patients with Alzheimer's disease.
What is a Battery-Powered RFID or an Active RFID Tag?
There are two main types of RFID tags: Passive and Active RFID tag. Passive tags are powered by energy from the RFID reader's interrogating radio waves. Active tags also called Battery-Powered RFID tags are powered by a battery and thus can be read at a greater range from the RFID reader, up to hundreds of meters. The trend for active RFID is moving towards greater integration with IoT systems, enabling more sophisticated data collection and real-time analytics. Advances in battery technology are also extending the operational life of these tags.
Active RFID in IoT: A Growing Convergence
Active RFID plays a crucial role in IoT by enabling real-time tracking, monitoring, and data collection across various industries. In IoT ecosystems, Active RFID tags provide continuous data streams about the location, status, and condition of assets, making them invaluable for applications that require precise, real-time information. The integration of Active RFID into IoT systems is steadily increasing across various industries. Key trends driving this convergence include:
●Industrial IoT (IIoT): Active RFID is being used extensively for asset tracking, inventory management, and supply chain visibility in manufacturing, logistics, and warehousing.
●Smart Cities: Applications include vehicle tracking, waste management, infrastructure monitoring, and public safety.
●Logistics and Supply Chain: Real-time tracking of goods, containers, and vehicles is enhancing supply chain efficiency and visibility.
●Agriculture: Livestock monitoring, equipment tracking, and crop management are benefiting from Active RFID and IoT integration.
Specific Cases
Industrial IoT (IIoT)
●Case Study: A large manufacturing company implemented Active RFID tags across its production facility to monitor the location and status of equipment, tools, and raw materials in real-time.
●Details: The tags were integrated with the company’s IoT platform, enabling real-time tracking and predictive maintenance. The system used edge computing to process data locally, reducing latency and improving decision-making.
●Outcome: Increased operational efficiency by 20% and reduced downtime due to equipment failure by 15%.
Smart Retail
●Case Study: A major retail chain used Active RFID tags to enhance inventory management and customer experience in its stores.
●Details: The RFID tags were attached to high-value items, providing real-time data on their location and movement. The tags communicated with the store’s IoT network, triggering automated reordering processes and personalized customer interactions.
●Outcome: Improved inventory accuracy by 30%, reduced stockouts by 25%, and enhanced customer satisfaction through personalized service.
Smart Farming
●Case Study: A large cattle farm implemented Active RFID tags to monitor and manage its herd in real-time.
●Details: Each cow was equipped with an Active RFID tag that tracked its location, movement patterns, and vital signs such as temperature and heart rate. The RFID tags communicated with IoT gateways placed around the farm, sending data to a central management system.
●Outcome: The farm saw a 25% reduction in livestock mortality, a 15% increase in milk production due to improved animal health, and a 20% reduction in labor costs associated with manual herd monitoring.
Smart City Transportation
●Case Study: A smart city project deployed Active RFID tags in public transportation systems to monitor the movement and status of buses and trains.
●Details: The RFID tags were integrated into the city’s IoT infrastructure, providing real-time data on vehicle locations, schedules, and passenger loads. This data was used to optimize routes, reduce congestion, and improve service reliability.
●Outcome: Increased public transportation efficiency by 15%, reduced travel times by 10%, and improved passenger satisfaction.
Healthcare IoT
●Case Study: A hospital implemented Active RFID tags to track and monitor critical assets such as wheelchairs, stretchers, and medical devices in real-time.
●Details: The tags were connected to the hospital’s IoT platform, providing real-time location data and usage statistics. The system enabled automated alerts for equipment shortages or maintenance needs.
●Outcome: Reduced equipment search times by 50%, increased asset utilization by 20%, and improved patient care efficiency.
What Batteries Are Used for RFID Tags?
Active RFID tags typically use small, low-power batteries designed to provide energy over an extended period. The most commonly used batteries are Lithium coin cells due to their long shelf life, stable voltage, and compact size, such as CR2032, CR2450 and CR2477. However, as IoT and smart systems continue to evolve, there is a growing need for RFID tags that can operate autonomously for extended periods without human intervention. This has led to the development of more efficient rechargeable batteries, such as lithium-ion or lithium-polymer batteries, with enhanced energy density, longer life cycles, and better performance in a range of temperatures.
Conclusion
The integration of Active RFID tags into IoT systems represents a significant leap forward in real-time data collection and asset management. As industries continue to adopt this technology, the role of batteries in ensuring the longevity and reliability of RFID tags becomes increasingly critical. From lithium coin cells to advanced rechargeable options, the choice of battery can greatly influence the performance and efficiency of Active RFID systems. Grepow specializes in manufacturing shaped lithium-ion batteries and lithium-polymer batteries that are as thin as 0.5 millimeters, as narrow as 4.5 millimeters, and can be produced in flexible, curved forms, ideal for a wide range of Active RFID tags. If you have any questions or needs, please feel free to contact us at info@grepow.com.
Related Articles
-

Building an FPV Drone: A Deep Dive into the Technology
2025-06-30 -

What is an 8S LiPo Battery?
2025-06-20 -

What Is the Voltage of a LiPo Battery?
2025-06-17
Related products
-

Pouch Rectangular Lipo Battery
-

Pouch Ultra Narrow Lipo Battery
-

Pouch Irregular Lipo Battery
-

Pouch Round Lipo Battery
-

Pouch Curved Lipo Battery
-
Pouch Ultra Thin Lipo Battery